Optische Kohärenztomographie (OCT)
Anwendung und Entwicklung von ultraschnellen MHz-OCT-Systemen
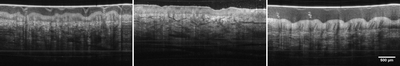
Die OCT ist ein nichtinvasives Bildgebungsverfahren, welches man typischerweise nutzt um dreidimensionale Tomogramme mit hoher Auflösung (~10µm) von stark streuendem Gewebe zu erstellen. Durch die Verwendung von eigens entwickelten FDML-Lasern erreichen wir Aufnahmegeschwindigkeiten von mehreren Millionen Tiefenscans pro Sekunde (MHz-OCT). Dies ist um ein bis zwei Größenordnungen schneller als derzeitige kommerzielle Systeme.
Diese hohen Geschwindigkeiten sind in vielen klinischen Bereichen (z.B. ophthalmisches und intravaskuläres OCT) nützlich, da sie die Aufnahmedauer verringern und helfen Bewegungsartefakte zu vermeiden. Die hohe Geschwindigkeit ermöglicht aber auch einen Zugang zur Phase des detektierten Lichts und damit neue numerische Methoden zur Bildverbesserung und Kontrastgebung in der Swept-Source-OCT.
Unsere Arbeitsgruppe forscht im Bereich der OCT an neuen Technologien und zeigt mögliche Anwendungsgebiete auf.
Forschungsschwerpunkte:
- MHz-OCT - Ultraschnelle OCT-Bildgebung mit mehreren millionen Tiefenschnitten pro Sekunde
- LARA-OCT - Großflächige OCT-Bildgebung von Haut mittel Roboter unterstützer MHz-OCT
- VR-OCT - Echtzeit Berechnung und Visualisierung ganzer OCT-Volumen in einer virtuellen Umgebung
- Augen OCT - Anwendung der MHz-OCT am Auge zur Darstellung der Netzhaut oder des Augenvordergrunds
- Phasensensitive OCT - Erweiterung des Informationsgehalts einer OCT-Aufnahme durch hinzufügen eines Phasenkontrastes
- Multispektrale OCT - Kombination aus RGB- und OCT-Aufnahmen zur verbesserten Darstellung morphologischer Strukturen
zugehörige Publikationen
2023
Characterization of brain tumor tissue by time-resolved, phase-sensitive optical coherence elastography at 3.2 MHz line rate, in Advanced Biomedical and Clinical Diagnostic and Surgical Guidance Systems XXI , Caroline Boudoux and James W. Tunnell, Eds. SPIE, Mä.2023. pp. 123680F.
| DOI: | 10.1117/12.2648301 |
| Bibtex: | @inproceedings{10.1117/12.2648301,
author = {Sazgar Burhan and Nicolas Detrez and Katharina Rewerts and Madita G{\"o}b and Christian Hagel and Matteo Mario Bonsanto and Dirk Theisen-Kunde and Robert Huber and Ralf Brinkmann},
title = {{Characterization of brain tumor tissue by time-resolved, phase-sensitive optical coherence elastography at 3.2 MHz line rate}},
volume = {12368},
booktitle = {Advanced Biomedical and Clinical Diagnostic and Surgical Guidance Systems XXI},
editor = {Caroline Boudoux and James W. Tunnell},
organization = {International Society for Optics and Photonics},
publisher = {SPIE},
pages = {123680F},
abstract = {Optical coherence elastography (OCE) offers the possibility of obtaining the mechanical behavior of a tissue. When also using a non-contact mechanical excitation, it mimics palpation without interobserver variability. One of the most frequently used techniques is phase-sensitive OCE. Depending on the system, depth-resolved changes in the sub-µm to nm range can be detected and visualized volumetrically. Such an approach is used in this work to investigate and detect transitions between healthy and tumorous brain tissue as well as inhomogeneities in the tumor itself to assist the operating surgeon during tumor resection in the future. We present time-resolved, phase-sensitive OCE measurements on various ex vivo brain tumor samples using an ultra-fast 3.2 MHz swept-source optical coherence tomography (SS-OCT) system with a frame rate of 2.45 kHz. 4 mm line scans are acquired which, in combination with the high imaging speed, allow monitoring and investigation of the sample's behavior in response to the mechanical load. Therefore, an air-jet system applies a 200 ms short air pulse to the sample, whose non-contact property facilitates the possibility for future in vivo measurements. Since we can temporally resolve the response of the sample over the entire acquisition time, the mechanical properties are evaluated at different time points with depth resolution. This is done by unwrapping the phase data and performing subsequent assessment. Systematic ex vivo brain tumor measurements were conducted and visualized as distribution maps. The study outcomes are supported by histological analyses and examined in detail.},
keywords = { Optical Coherence Tomography, Optical Coherence Elastography, Phase-sensitive OCT, Fourier Domain Mode Locking, Brain Tumor, Phase Unwrapping, Tissue Characterization, Biomechanics},
year = {2023},
doi = {10.1117/12.2648301},
URL = {https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2648301}
}
|
Large area robotically assisted optical coherence tomography (LARA-OCT) for skin imaging with MHz-OCT surface tracking, in Optical Coherence Tomography and Coherence Domain Optical Methods in Biomedicine XXVII , Joseph A. Izatt and James G. Fujimoto, Eds. SPIE, Mä.2023. pp. 123670C.
| DOI: | 10.1117/12.2652616 |
| Bibtex: | @inproceedings{10.1117/12.2652616,
author = {Madita G{\"o}b and Simon Lotz and Linh Ha-Wissel and Sazgar Burhan and Sven B{\"o}ttger and Floris Ernst and Jennifer Hundt and Robert Huber},
title = {{Large area robotically assisted optical coherence tomography (LARA-OCT) for skin imaging with MHz-OCT surface tracking}},
volume = {12367},
booktitle = {Optical Coherence Tomography and Coherence Domain Optical Methods in Biomedicine XXVII},
editor = {Joseph A. Izatt and James G. Fujimoto},
organization = {International Society for Optics and Photonics},
publisher = {SPIE},
pages = {123670C},
abstract = {Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a powerful imaging technique to non-invasively differentiate between healthy skin and pathological conditions. Unfortunately, commercially available OCT-systems are typically slow and not capable of scanning large areas at reasonable speed. Since skin lesions may extend over several square centimeters, potential inflammatory infiltrates remain undetected. Here, we present large area robotically assisted OCT (LARA-OCT) for skin imaging. Therefor a collaborative robot is combined with an existing, home-built 3.3 MHz-OCT-system and for surface tracking an online probe-to-surface control is implemented which is solely based on the OCT surface signal. It features a combined surface-distance and surface-orientation closed-loop control algorithm, which enables automatic positioning and alignment of the probe across the target while imaging. This allows to acquire coherent OCT images of skin areas beyond 10 cm<sup>2</sup>. },
keywords = {Optical Coherence Tomography, Fourier Domain Mode Locking, Robotically Assisted Imaging Systems, Three-dimensional image acquisition, Large Area Scanning, Skin Imaging , OCT, FDML},
year = {2023},
doi = {10.1117/12.2652616},
URL = {https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2652616}
}
|
Synchronous high-speed OCT imaging with sensor less brushless DC motor and FDML laser in a phase-locked loop, in Optical Coherence Tomography and Coherence Domain Optical Methods in Biomedicine XXVII , Joseph A. Izatt and James G. Fujimoto, Eds. SPIE, Mä.2023. pp. 1236703.
| DOI: | 10.1117/12.2652955 |
| Bibtex: | @inproceedings{10.1117/12.2652955,
author = {Awanish Pratap Singh and Madita G{\"o}b and Martin Ahrens and Tim Eixmann and Hinnerk Schulz-Hildebrandt and Gereon H{\"u}ttmann and Robert Huber and Maik Rahlves},
title = {{Synchronous high-speed OCT imaging with sensor less brushless DC motor and FDML laser in a phase-locked loop}},
volume = {12367},
booktitle = {Optical Coherence Tomography and Coherence Domain Optical Methods in Biomedicine XXVII},
editor = {Joseph A. Izatt and James G. Fujimoto},
organization = {International Society for Optics and Photonics},
publisher = {SPIE},
pages = {1236703},
abstract = {High-speed endoscopic optical coherence tomography (OCT) imaging in the MHz range has shown great potential in various medical applications ranging from cancer screening to vascular disease monitoring. High-speed imaging always suffers from non-uniform rotational distortion (NURD) due to asynchronous motor rotation with the OCT system. Several research groups have previously attempted to solve this problem, using either an expensive motor with a sensor or numerical correction after data acquisition. However, both techniques pose challenges for practical use. Therefore, in this study, we use an inexpensive sensorless brushless DC motor with a Fourier domain mode-locked (FDML) laser-based MHz OCT system and try to resolve the problem of synchronization using three different modalities, (i) Slave-mode: The FDML frequency serves as a master frequency for the motor, which is phase-locked to the FDML frequency, (ii) Master-mode: The revolution trigger obtained from the motor’s back electromotive force (BEMF) signal serves as a trigger signal for the OCT imaging system, (iii) Both: Fully synchronized setup, where the motor rotation is synchronized with the laser and the imaging system is synchronized with the motor to achieve phase-stable OCT imaging. The first case slightly fluctuates in live preview and imaging due to the absence of a revolution trigger, while the second has varying motor speeds. Therefore, we use the third case to phase-lock the motor with FDML and get a distortion-free live preview and image acquisition. Finally, we demonstrate high-speed SS-OCT structural imaging (at 3.3 MHz A-scan rates) of a finger with a 16 mm diameter probe (at 40,000 rpm).},
keywords = {Optical Coherence Tomography, Endoscopy, FDML , Closed Loop Motor Control, NURD compensation, Brushless DC Motor, Back Electromotive Force},
year = {2023},
doi = {10.1117/12.2652955},
URL = {https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2652955}
} |
Dual wavelength analysis and classification of brain tumor tissue with optical coherence tomography, in Advanced Biomedical and Clinical Diagnostic and Surgical Guidance Systems XXI , Caroline Boudoux and James W. Tunnell, Eds. SPIE, Mä.2023. pp. 1236805.
| DOI: | 10.1117/12.2649963 |
| Bibtex: | @inproceedings{10.1117/12.2649963,
author = {Paul Strenge and Birgit Lange and Wolfgang Draxinger and Christian Hagel and Christin Grill and Veit Danicke and Dirk Theisen-Kunde and Sonja Spahr-Hess and Matteo M. Bonsanto and Robert Huber and Heinz Handels and Ralf Brinkmann},
title = {{Dual wavelength analysis and classification of brain tumor tissue with optical coherence tomography}},
volume = {12368},
booktitle = {Advanced Biomedical and Clinical Diagnostic and Surgical Guidance Systems XXI},
editor = {Caroline Boudoux and James W. Tunnell},
organization = {International Society for Optics and Photonics},
publisher = {SPIE},
pages = {1236805},
abstract = {The ill-defined tumor borders of glioblastoma multiforme pose a major challenge for the surgeon during tumor resection, since the goal of the tumor resection is the complete removal, while saving as much healthy brain tissue as possible. In recent years, optical coherence tomography (OCT) was successfully used to classify white matter from tumor infiltrated white matter by several research groups. Motivated by these results, a dataset was created, which consisted of sets of corresponding ex vivo OCT images, which were acquired by two OCT-systems with different properties (e.g. wavelength and resolution). Each image was annotated with semantic labels. The labels differentiate between white and gray matter and three different stages of tumor infiltration. The data from both systems not only allowed a comparison of the ability of a system to identify the different tissue types present during the tumor resection, but also enable a multimodal tissue analysis evaluating corresponding OCT images of the two systems simultaneously. A convolutional neural network with dirichlet prior was trained, which allowed to capture the uncertainty of a prediction. The approach increased the sensitivity of identifying tumor infiltration from 58 % to 78 % for data with a low prediction uncertainty compared to a previous monomodal approach. },
keywords = {optical coherence tomography, oct, brain, classification, tumor, dual wavelength, glioblastoma multiforme, tissue analysis},
year = {2023},
doi = {10.1117/12.2649963},
URL = {https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2649963}
} |
Air-jet based optical coherence elastography of brain tumor tissue: stiffness evaluation by structural histological analysis, in Emerging Technologies for Cell and Tissue Characterization II , Seemantini K. Nadkarni and Giuliano Scarcelli, Eds. SPIE, 2023. pp. 126290M.
| DOI: | 10.1117/12.2670944 |
| Datei: | 12.2670944 |
| Bibtex: | @inproceedings{10.1117/12.2670944,
author = {Nicolas Detrez and Sazgar Burhan and Paul Strenge and Jessica Kren and Christian Hagel and Matteo Mario Bonsanto and Dirk Theisen-Kunde and Robert Huber and Ralf Brinkmann},
title = {{Air-jet based optical coherence elastography of brain tumor tissue: stiffness evaluation by structural histological analysis}},
volume = {12629},
booktitle = {Emerging Technologies for Cell and Tissue Characterization II},
editor = {Seemantini K. Nadkarni and Giuliano Scarcelli},
organization = {International Society for Optics and Photonics},
publisher = {SPIE},
pages = {126290M},
keywords = {Optical Coherence Elastography, Air-Jet, Phase-sensitive OCT, Histology Structure Analysis, Color-Deconvolution, Structural Tensors, Brain tumor, Tissue Characterization},
year = {2023},
doi = {10.1117/12.2670944},
URL = {https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2670944}
} |
Air-Jet based optical coherence elastography: processing and mechanical interpretation of brain tumor data, in Optical Elastography and Tissue Biomechanics X , Kirill V. Larin and Giuliano Scarcelli and Frédérique Vanholsbeeck, Eds. SPIE, 2023. pp. 1238105.
| DOI: | 10.1117/12.2649835 |
| Datei: | 12.2649835 |
| Bibtex: | @inproceedings{10.1117/12.2649835,
author = {Nicolas Detrez and Sazgar Burhan and Katharina Rewerts and Jessica Kren and Christian Hagel and Matteo Mario Bonsanto and Dirk Theisen-Kunde and Robert Huber and Ralf Brinkmann},
title = {{Air-Jet based optical coherence elastography: processing and mechanical interpretation of brain tumor data}},
volume = {12381},
booktitle = {Optical Elastography and Tissue Biomechanics X},
editor = {Kirill V. Larin and Giuliano Scarcelli and Fr{\'e}d{\'e}rique Vanholsbeeck},
organization = {International Society for Optics and Photonics},
publisher = {SPIE},
pages = {1238105},
keywords = {Optical Coherence Elastography, Air-Jet, Air-Puff, biomechanics, viscoelasticity, rheology, brain tissue, brain tumor},
year = {2023},
doi = {10.1117/12.2649835},
URL = {https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2649835}
} |
MHz time stretch swept source using a commercial erbium-doped fiber amplifier, in Optical Coherence Tomography and Coherence Domain Optical Methods in Biomedicine XXVII , Joseph A. Izatt and James G. Fujimoto, Eds. SPIE, 2023. pp. 1236706.
| DOI: | 10.1117/12.2651127 |
| Datei: | 12.2651127 |
| Bibtex: | @inproceedings{10.1117/12.2651127,
author = {A. Mart{\'i}nez Jim{\'e}nez and M. Spacek and M. Wacker and R. Huber and A. Bradu and A. Podoleanu},
title = {{MHz time stretch swept source using a commercial erbium-doped fiber amplifier}},
volume = {12367},
booktitle = {Optical Coherence Tomography and Coherence Domain Optical Methods in Biomedicine XXVII},
editor = {Joseph A. Izatt and James G. Fujimoto},
organization = {International Society for Optics and Photonics},
publisher = {SPIE},
pages = {1236706},
keywords = {swept source, time-stretch, optical coherence tomography, mode-locking},
year = {2023},
doi = {10.1117/12.2651127},
URL = {https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2651127}
} |
Phase analysis strategies for MHz OCE in the large displacement regime, in Optical Coherence Tomography and Coherence Domain Optical Methods in Biomedicine XXVII , Joseph A. Izatt and James G. Fujimoto, Eds. SPIE, 2023. pp. 123670Q.
| DOI: | 10.1117/12.2652847 |
| Bibtex: | @inproceedings{10.1117/12.2652847,
author = {Sazgar Burhan and Nicolas Detrez and Katharina Rewerts and Madita G{\"o}b and Steffen Buschschl{\"u}ter and Christian Hagel and Matteo Mario Bonsanto M.D. and Dirk Theisen-Kunde and Robert Huber and Ralf Brinkmann},
title = {{Phase analysis strategies for MHz OCE in the large displacement regime}},
volume = {12367},
booktitle = {Optical Coherence Tomography and Coherence Domain Optical Methods in Biomedicine XXVII},
editor = {Joseph A. Izatt and James G. Fujimoto},
organization = {International Society for Optics and Photonics},
publisher = {SPIE},
pages = {123670Q},
abstract = {In neurosurgical tumor operations on the central nervous system, intraoperative haptic information often assists for discrimination between healthy and diseased tissue. Thus, it can provide the neurosurgeon with additional intraoperative source of information during resection, next to the visual information by the light microscope, fluorescent dyes and neuronavigation. One approach to obtain elastic and viscoelastic tissue characteristics non-subjectively is phase-sensitive optical coherence elastography (OCE), which is based on the principle of optical coherence tomography (OCT). While phase-sensitive OCE offers significantly higher displacement sensitivity inside a sample than commonly used intensity-based correlation methods, it requires a reliable algorithm to recover the phase signal, which is mathematically restricted in the -π to π range. This problem of phase wrapping is especially critical for inter-frame phase analysis since the time intervals between two referenced voxels is long. Here, we demonstrate a one-dimensional unwrapping algorithm capable of removing up to 4π-ambiguities between two frames in the complex phase data obtained from a 3.2 MHz-OCT system. The high sampling rate allows us to resolve large sample displacements induced by a 200 ms air pulse and acquires pixel-precise detail information. The deformation behavior of the tissue can be monitored over the entire acquisition time, offering various subsequent mechanical analysis procedures. The reliability of the algorithm and imaging concept was initially evaluated using different brain tumor mimicking phantoms. Additionally, results from human ex vivo brain tumor samples are presented and correlated with histological findings supporting the robustness of the algorithm.},
keywords = {Optical Coherence Tomography, Megahertz OCT, Fourier Domain Mode Locking, Optical Coherence Elastography, Phase-sensitive OCT, Phase Unwrapping, Brain tumor, Biomechanics},
year = {2023},
doi = {10.1117/12.2652847},
URL = {https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2652847}
} |
2022
Influence of the linewidth enhancement factor on the signal pattern of Fourier domain mode-locked lasers, Applied Physics B , vol. 18(12), Nov. 2022.
| DOI: | 10.1007/s00340-022-07933-5 |
| Bibtex: | @article{RN5426,
author = {Aşırım, Özüm Emre;Huber, Robert and Jirauschek, Christian},
title = {Influence of the linewidth enhancement factor on the signal pattern of Fourier domain mode-locked lasers},
journal = {Applied Physics B},
volume = {128},
number = {12},
pages = {218},
ISSN = {1432-0649},
DOI = {10.1007/s00340-022-07933-5},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-022-07933-5},
year = {2022},
type = {Journal Article}
}
|
620 Screening an inhibitor library for new drug candidates to promote wound healing, Journal of Investigative Dermatology , vol. 142, no. 12, Supplement, pp. S288, Nov. 2022.
| DOI: | https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2022.09.637 |
| Datei: | S0022202X22025714 |
| Bibtex: | @article{JACOBI2022S288,
title = {620 Screening an inhibitor library for new drug candidates to promote wound healing},
journal = {Journal of Investigative Dermatology},
volume = {142},
number = {12, Supplement },
pages = {S288},
year = {2022},
note = {ESDR 2022 Meeting Abstract Supplement},
issn = {0022-202X},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2022.09.637},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022202X22025714},
author = {C. Jacobi and M. Göb and R. Huber and R.J. Ludwig and J.E. Hundt}
} |
Intravascular optical coherence elastography, Biomed. Opt. Express , vol. 13, no. 10, pp. 5418--5433, Okt. 2022. Optica Publishing Group.
| DOI: | 10.1364/BOE.470039 |
| Datei: | abstract.cfm |
| Bibtex: | Optical coherence elastography (OCE), a functional extension of optical coherence tomography (OCT), visualizes tissue strain to deduce the tissue’s biomechanical properties. In this study, we demonstrate intravascular OCE using a 1.1 mm motorized catheter and a 1.6 MHz Fourier domain mode-locked OCT system. We induced an intraluminal pressure change by varying the infusion rate from the proximal end of the catheter. We analysed the pixel-matched phase change between two different frames to yield the radial strain. Imaging experiments were carried out in a phantom and in human coronary arteries in vitro. At an imaging speed of 3019 frames/s, we were able to capture the dynamic strain. Stiff inclusions in the phantom and calcification in atherosclerotic plaques are associated with low strain values and can be distinguished from the surrounding soft material, which exhibits elevated strain. For the first time, circumferential intravascular OCE images are provided side by side with conventional OCT images, simultaneously mapping both the tissue structure and stiffness. |
Case report: Optical coherence tomography for monitoring biologic therapy in psoriasis and atopic dermatitis, Frontiers in Medicine , vol. 9, Sep. 2022.
| DOI: | 10.3389/fmed.2022.995883 |
| Datei: | fmed.2022.995883 |
| Bibtex: | @article{RN5359,
author = {Ha-Wissel, L.;Yasak, H.;Huber, R.;Zillikens, D.;Ludwig, R. J.;Thaçi, D. and Hundt, J. E.},
title = {Case report: Optical coherence tomography for monitoring biologic therapy in psoriasis and atopic dermatitis},
journal = {Front Med (Lausanne)},
volume = {9},
pages = {995883},
ISSN = {2296-858X (Print)
2296-858x},
DOI = {10.3389/fmed.2022.995883},
year = {2022},
type = {Journal Article}
}
|
Differentiation of different stages of brain tumor infiltration using optical coherence tomography: Comparison of two systems and histology, Frontiers in Oncology , Aug. 2022.
| DOI: | 10.3389/fonc.2022.896060 |
| Bibtex: | @article{Strenge-2022,
author = {Strenge, P.;Lange, B.;Grill,C.;Danicke,V.;Theisen-Kunde, D.;Hagel, C.;Spahr-Hess, S.;;Bonsanto, Matteo M.;Handels, H.; and Huber, R.;Brinkmann, R.},
title = {Differentiation of different stages of brain tumor infiltration using optical coherence tomography: Comparison of two systems and histology},
journal = {Frontiers in Oncology},
Keywords = {AG-Huber_FDML, AG-Huber_OCT, brain, tumor, glioblastoma multiforme, OCT, neural network, attenuation (absorption)
coefficient, optical coherence tomography},
DOI = {https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.896060},
url = {https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2022.896060/full},
year = {2022},
type = {Journal Article}
}
|
Registration of histological brain images onto optical coherence tomography images based on shape information, Physics in Medicine & Biology , Jun. 2022.
| DOI: | 10.1088/1361-6560/ac6d9d |
| Bibtex: | @article{Strenge2022,
author = {Strenge, P;Lange, B;Grill, C;Draxinger, W;Danicke, V;Theisen-Kunde, D;Hagel, C;Spahr-Hess, S;Bonsanto, Matteo M.;Huber, R;Handels, H and Brinkmann, R},
title = {Registration of histological brain images onto optical coherence tomography images based on shape information},
keywords = {brain, glioblastoma multiforme, shape, OCT, optical coherence tomography, AG-Huber_OCT,},
journal = {Physics in Medicine & Biology},
ISSN = {0031-9155},
url = {http://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1361-6560/ac6d9d},
year = {2022},
type = {Journal Article}
}
|
Towards ultra-large area vascular contrast skin imaging using multi-MHz-OCT, in Optical Coherence Tomography and Coherence Domain Optical Methods in Biomedicine XXVI , Joseph A. Izatt and James G. Fujimoto, Eds. SPIE, Mä.2022. pp. 27 -- 31.
| DOI: | 10.1117/12.2612171 |
| Bibtex: | @inproceedings{10.1117/12.2612171,
author = {Madita G{\"o}b and Sazgar Burhan and Simon Lotz and Robert Huber},
title = {{Towards ultra-large area vascular contrast skin imaging using multi-MHz-OCT}},
volume = {11948},
booktitle = {Optical Coherence Tomography and Coherence Domain Optical Methods in Biomedicine XXVI},
editor = {Joseph A. Izatt and James G. Fujimoto},
organization = {International Society for Optics and Photonics},
publisher = {SPIE},
pages = {1194807},
abstract = {We demonstrate ultra-large field of view OCT scanning using standard optics, a X-Y-galvanometer scanner and a synchronously driven motorized XYZ-positioning stage. The integration of a movable stage into our self-built 3.3 MHz- OCT system allows acquiring coherent ultra-large area images, fully leveraging the high speed potential of our system. For fast OCT-angiography, one galvanometer axis scanner is driven in a repetitive sawtooth pattern, fully synchronized to the movement of the linear stage, to obtain multiple measurements at each position. This technique requires exact synchronization, precise repositioning, and uniform movements with low tolerances to ensure a minimum revisitation error. We analyze error and performance of our setup and demonstrate angiographic imaging.},
keywords = {Optical Coherence Tomography, Fourier Domain Mode Locking, FDML, Optical Coherence Angiography, OCTA, Medical optics and biotechnology, Medical imaging, Three-dimensional image acquisition, Scanners, Microscopy},
year = {2022},
doi = {10.1117/12.2612171},
URL = {https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2612171}
}
|
Continuous spectral zooming for in vivo live 4D-OCT with MHz A-scan rates and long coherence, Biomed. Opt. Express , vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 713--727, Feb. 2022. OSA.
| DOI: | 10.1364/BOE.448353 |
| Bibtex: | @article{Gob:22,
author = {Madita G\"{o}b and Tom Pfeiffer and Wolfgang Draxinger and Simon Lotz and Jan Philip Kolb and Robert Huber},
journal = {Biomed. Opt. Express},
keywords = {High speed imaging; Image processing; Image quality; In vivo imaging; Range imaging; Vertical cavity surface emitting lasers},
number = {2},
pages = {713--727},
publisher = {Optica Publishing Group},
title = {Continuous spectral zooming for in vivo live 4D-OCT with MHz A-scan rates and long coherence},
volume = {13},
month = {Feb},
year = {2022},
url = {https://opg.optica.org/boe/abstract.cfm?URI=boe-13-2-713},
doi = {10.1364/BOE.448353},
abstract = {We present continuous three-dimensional spectral zooming in live 4D-OCT using a home-built FDML based OCT system with 3.28 MHz A-scan rate. Improved coherence characteristics of the FDML laser allow for imaging ranges up to 10 cm. For the axial spectral zoom feature, we switch between high resolution and long imaging range by adjusting the sweep range of our laser. We present a new imaging setup allowing for synchronized adjustments of the imaging range and lateral field of view during live OCT imaging. For this, a novel inline recalibration algorithm was implemented that enables numerical k-linearization of the raw OCT fringes for every frame instead of every volume. This is realized by acquiring recalibration data within the dead time of the raster scan at the turning points of the fast axis scanner. We demonstrate in vivo OCT images of fingers and hands at different resolution modes and show real three-dimensional zooming during live 4D-OCT. A three-dimensional spectral zooming feature for live 4D-OCT is expected to be a useful tool for a wide range of biomedical, scientific and research applications, especially in OCT guided surgery.},
} |
OCT-Guided Surgery for Gliomas: Current Concept and Future Perspectives, Diagnostics , vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 335, Jan. 2022.
| DOI: | 10.3390/diagnostics12020335 |
| Datei: | 335 |
| Bibtex: | @article{Yashin-2022,
author = {Yashin, K;Bonsanto, M M;Achkasova, K;Zolotova, A;Wael, Al-M;Kiseleva, E;Moiseev, A;Medyanik, I;Kravets, L;Huber, R;Brinkmann, R and Gladkova, N},
title = {OCT-Guided Surgery for Gliomas: Current Concept and Future Perspectives},
journal = {Diagnostics},
volume = {12},
number = {2},
pages = {335},
ISSN = {2075-4418},
keywords = {AG-Huber; optical coherence tomography; brain imaging; neurosurgical guidance; brain tumor; minimally invasive theranostics; intraoperative imaging},
url = {https://www.mdpi.com/2075-4418/12/2/335},
year = {2022},
type = {Journal Article}
}
|
Effect of Self-Phase Modulation on The Signal Quality of Fourier Domain Mode-Locked Lasers, in 2022 International Conference on Numerical Simulation of Optoelectronic Devices (NUSOD) , 2022. pp. 67-68.
| DOI: | 10.1109/NUSOD54938.2022.9894816 |
| Bibtex: | @INPROCEEDINGS{9894816,
author={Aşırım, Ö. E. and Huber, R. and Jirauschek, C.},
booktitle={2022 International Conference on Numerical Simulation of Optoelectronic Devices (NUSOD)},
title={Effect of Self-Phase Modulation on The Signal Quality of Fourier Domain Mode-Locked Lasers},
year={2022},
volume={},
number={},
pages={67-68},
doi={10.1109/NUSOD54938.2022.9894816}} |
2021
Comparison of two optical coherence tomography systems to identify human brain tumor, Optical Society of America, Dez.2021. pp. EW1C.7.
| DOI: | 10.1117/12.2616044 |
| Bibtex: | @inproceedings{Strenge:21,
author = {P. Strenge, B. Lange, C. Grill, W. Draxinger, V. Danicke, D. Theisen-Kunde, H. Handels, M. M. Bonsanto, C. Hagel, R. Huber and R. Brinkmann},
journal = {European Conferences on Biomedical Optics 2021 (ECBO)},
keywords = {AG-Huber_OCT; Absorption coefficient; Attenuation coefficient; Fourier domain mode locking; Multiple scattering; Optical coherence tomography; Spectral domain optical coherence tomography},
pages = {EW1C.7},
publisher = {Optical Society of America},
title = {Comparison of two optical coherence tomography systems to identify human brain tumor},
year = {2021},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2616044},
abstract = {The identification of ex vivo brain tumor tissue was investigated with two different optical coherence tomography systems exploiting two optical parameters. The optical parameters were calculated from semantically labelled OCT B-scans.},
} |
Towards densely sampled ultra-large area multi-MHz-OCT for in vivo skin measurements beyond 1 cm2/sec, in European Conferences on Biomedical Optics 2021 (ECBO) , Optical Society of America, Dez.2021. pp. EW3C.4.
| DOI: | 10.1117/12.2616054 |
| Bibtex: | @inproceedings{Gob:21,
author = {Madita G\"{o}b and Sazgar Burhan and Wolfgang Draxinger and Jan Philip Kolb and Robert Huber},
booktitle = {European Conferences on Biomedical Optics 2021 (ECBO)},
journal = {European Conferences on Biomedical Optics 2021 (ECBO)},
keywords = {AG-Huber_OCT;Fourier domain mode locking; Image processing; Image quality; Optical coherence tomography; Temporal resolution; Three dimensional imaging},
pages = {EW3C.4},
publisher = {Optical Society of America},
title = {Towards densely sampled ultra-large area multi-MHz-OCT for in vivo skin measurements beyond 1 cm$^2$/sec},
year = {2021},
url = {http://www.osapublishing.org/abstract.cfm?URI=ECBO-2021-EW3C.4},
abstract = {We demonstrate a 3.3 MHz A-scan rate OCT for rapid scanning of large areas of human skin. The mosaicking performance and different OCT imaging modalities including intervolume speckle contrast are evaluated.},
} |
Flow Controlled Air Puff Generator Towards In Situ Brain Tumor Detection Based on MHz Optical Coherence Elastography, in ECBO , Optical Society of America, Dez.2021. pp. EW4A.10.
| Weblink: | https://opg.optica.org/abstract.cfm?uri=ECBO-2021-EW4A.10 |
| Bibtex: | @inproceedings{Detrez:21,
author = {N. Detrez, K. Rewerts, M. Matthiae, S. Buschschlueter, M.M. Bonsanto, D. Theisen-Kunde and R. Brinkmann},
journal = {European Conferences on Biomedical Optics 2021 (ECBO)},
keywords = {AG-Huber_OCT},
pages = {EW4A.10},
publisher = {Optical Society of America},
title = {Flow Controlled Air Puff Generator Towards In Situ Brain Tumor Detection Based on MHz Optical Coherence Elastography},
year = {2021},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2615022},
abstract = {A precision air puff excitation system for MHz Optical Coherence Elastography in neurosurgery was developed. It enables non-contact soft-tissue excitation down to {\textmu}N, with direct, noncontact force determination via gas flow measurement.},
} |
Phase-Sensitive Optical Coherence Elastography with a 3.2 MHz FDML-Laser Using Focused Air-Puff Tissue Indentation, in ECBO , Optical Society of America, Dez.2021. pp. ETh3A.3.
| Weblink: | https://opg.optica.org/abstract.cfm?URI=ECBO-2021-ETh3A.3 |
| Bibtex: | @inproceedings{Rewerts2021ECBO,
author = {K. Rewerts, M. Matthiae, N. Detrez, S. Buschschlueter, M.M. Bonsanto, R. Huber and R. Brinkmann},
journal = {European Conferences on Biomedical Optics 2021 (ECBO)},
keywords = {AG-Huber_OCT},
pages = {ETh3A.3},
publisher = {Optical Society of America},
title = {Phase-Sensitive Optical Coherence Elastography with a 3.2 MHz FDML-Laser Using Focused Air-Puff Tissue Indentation},
year = {2021},
url = {http://www.osapublishing.org/abstract.cfm?URI=ECBO-2021-ETh3A.3},
abstract = {Tumor discrimination from healthy tissue is often performed by haptically probing tissue elasticity. We demonstrate non-contact elastography using air-puff excitation and tissue indentation measurement by phase-sensitive OCT with a 3.2 MHz FDML-laser.},
} |
High finesse tunable Fabry-Perot filters in Fourier-domain modelocked lasers, in Optical Coherence Tomography and Coherence Domain Optical Methods in Biomedicine XXV , Joseph A. Izatt and James G. Fujimoto, Eds. SPIE, Jun.2021.
| DOI: | 10.1117/12.2583501 |
| Bibtex: | @inproceedings{Pfeiffer2021,
author = {T. Pfeiffer, T. Klein, A. Mlynek, W. Wieser, S. Lotz, C. Grill and R. Huber},
title = {{High finesse tunable Fabry-Perot filters in Fourier-domain modelocked lasers}},
volume = {11630},
booktitle = {Optical Coherence Tomography and Coherence Domain Optical Methods in Biomedicine XXV},
editor = {Joseph A. Izatt and James G. Fujimoto},
organization = {International Society for Optics and Photonics},
publisher = {SPIE},
abstract = {We demonstrate that the coherence roll-off and dynamic range of OCT systems using Fourier-domain mode-locked (FDML) lasers can be significantly improved by a fiber Fabry-Perot tunable filter (FFP-TF) with a finesse of more than 3000, a more than fivefold improvement over previous designs. In contrast to previous work, standard resampling using a pre-acquired signal (as in SD-OCT) with no k-clocking is sufficient for 20 nm and 100 nm sweep range, significantly reducing the system complexity. 3D-OCT imaging at 20 cm imaging range is demonstrated.},
keywords = {AG-Huber_FDML, AG-Huber_OCT, optical coherence tomography, FDML laser, swept source laser, high finesse, Fabry-Perot, MHz-OCT, OCT, tunable laser},
year = {2021},
URL = {hhttps://doi.org/10.1117/12.2583501}
} |
Characterization of brain tumor tissue with 1310 nm optical coherence tomography, in Optical Coherence Tomography and Coherence Domain Optical Methods in Biomedicine XXV , Joseph A. Izatt and James G. Fujimoto, Eds. SPIE, Mä.2021. pp. 74 -- 80.
| DOI: | 10.1117/12.2578409 |
| Bibtex: | @inproceedings{Strenge2021A,
author = {P. Strenge, B. Lange, C. Grill, W. Draxinger, V. Danicke, D. Theisen-Kunde, H. Handels, M. Bonsanto, C. Hagel, R. Huber and R. Brinkmann},
title = {{Characterization of brain tumor tissue with 1310 nm optical coherence tomography}},
volume = {11630},
booktitle = {Optical Coherence Tomography and Coherence Domain Optical Methods in Biomedicine XXV},
editor = {Joseph A. Izatt and James G. Fujimoto},
organization = {International Society for Optics and Photonics},
publisher = {SPIE},
pages = {74 -- 80},
abstract = {The separation of tumorous brain tissue and healthy brain tissue is still a big challenge in the field of neurosurgery, especially when it comes to the detection of different infiltration grades of glioblastoma multiforme at the tumor border. On the basis of a recently created labelled OCT dataset of ex vivo glioblastoma multiforme tumor samples the detection of brain tumor tissue and the identification of zones with varying degrees of infiltration of tumor cells was investigated. The identification was based on the optical properties, which were extracted by an exponential fit function. The results showed that a separation of tumorous tissue and healthy white matter based on these optical properties is possible. A support vector machine was trained on the optical properties to separate tumor from healthy white matter tissue, which achieved a sensitivity of 91% and a specificity of 76% on an independent training dataset.},
keywords = {AG-Huber_OCT, optical coherence tomography, OCT, glioblastoma multiforme, MHz-OCT, brain imaging, tumor, neurosurgery},
year = {2021},
URL = {hhttps://doi.org/10.1117/12.2578409}
} |
Combination of two-photon microscopy and optical coherence tomography with fully fiber-based lasers for future endoscopic setups, in Multimodal Biomedical Imaging XVI , SPIE, Mä.2021.
| DOI: | 10.1117/12.2578679 |
| Bibtex: | @Conference{Lamminger2021,
author = {P. Lamminger, M. Loop, J. Klee, D. Weng, J.P. Kolb, M. Strauch, S. Karpf and R. Huber},
booktitle = {Multimodal Biomedical Imaging XVI},
title = {Combination of two-photon microscopy and optical coherence tomography with fully fiber-based lasers for future endoscopic setups},
year = {2021},
publisher = {SPIE},
doi = {10.1117/12.2578679},
keywords = {AG-Huber_NL, AG-Huber_OCT},
} |
Mitarbeiter
Wolfgang Draxinger

AG Huber
Gebäude 81
,
Raum 72
wolfgang.draxinger(at)uni-luebeck.de
+49 451 3101 3229
Madita Göb

AG Huber
Gebäude 81
,
Raum 61
m.goeb(at)uni-luebeck.de
+49 451 3101 3262
Sazgar Burhan

AG Huber
Gebäude 81
,
Raum 61
sa.burhan(at)uni-luebeck.de
+49 451 3101 3263
Simon Lotz

AG Huber
Gebäude 81
,
Raum 72
si.lotz(at)uni-luebeck.de
+49 451 3101 3231
Marie Klufts

AG Huber
Gebäude 81
,
Raum 61
marie.klufts(at)uni-luebeck.de
+49 451 3101 3264